THE NATURAL GLUCOSE RESET: How Plant Compounds Are Reshaping Blood Sugar Control in Adults Over 40
By Dr. James Holloway, MD – Endocrinology & Metabolic Health | Independent Contributor
“Blood sugar spikes aren’t just about carbs. They’re about metabolic damage — and science is finally showing us how to fix it naturally.”
INTRODUCTION: THE HIDDEN METABOLIC CRISIS
After 40, it becomes increasingly difficult to maintain stable blood sugar. This isn’t just about eating habits — it’s about deeper metabolic changes.
What new research reveals is that insulin resistance, glucose intolerance, and post-meal spikes are the result of:
- Mitochondrial inefficiency
- Chronic inflammation
- Cellular stress
- And impaired glucose transport
A growing field of clinical studies is now validating what natural medicine has long suggested: certain plant-based compounds can directly support insulin sensitivity, glucose uptake, and metabolic balance — without aggressive drugs or side effects.
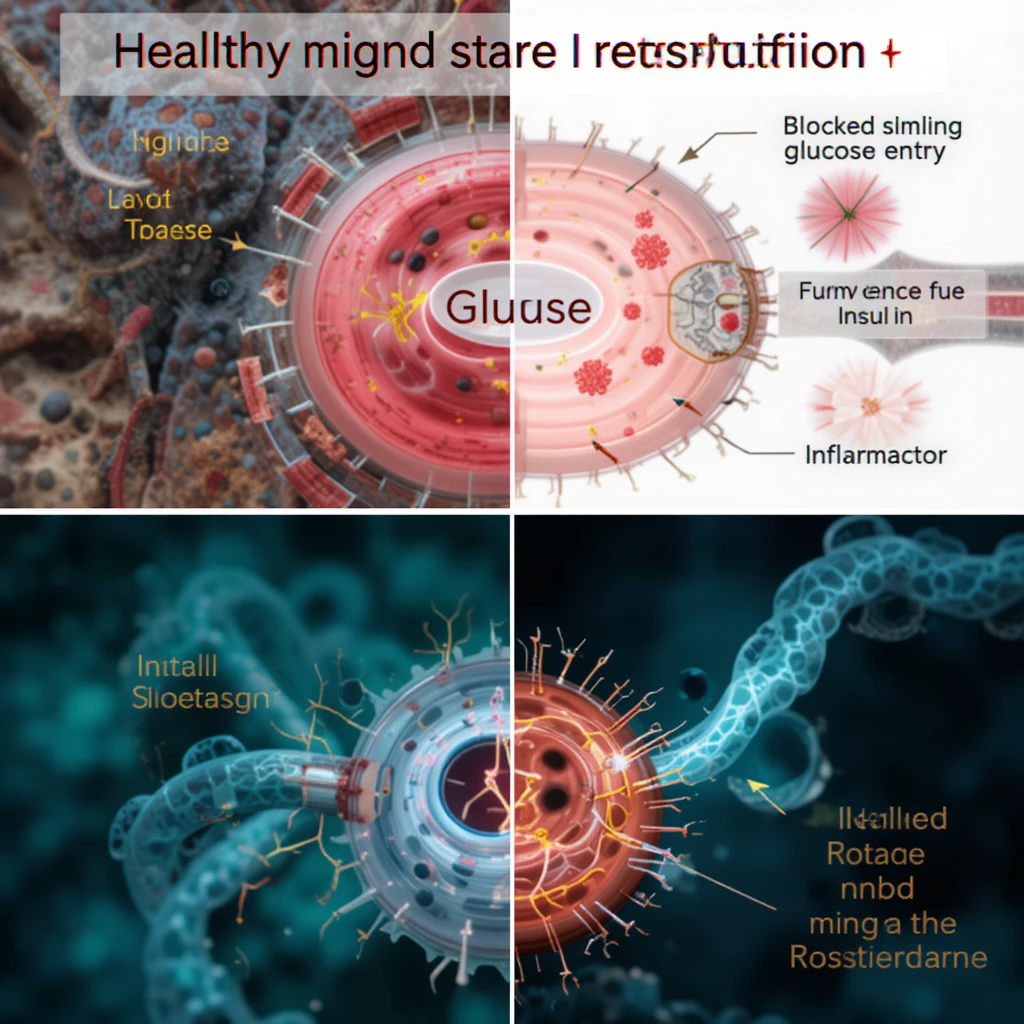
THE SCIENCE OF NATURAL GLUCOSE MANAGEMENT

.
Unlike synthetic drugs that act on one pathway, botanical-based metabolic support works through multiple mechanisms:
- Stimulating glucose uptake at the cellular level
- Enhancing insulin signaling
- Reducing inflammatory cytokines
- Protecting pancreatic β-cells
- Improving mitochondrial glucose oxidation
This multi-targeted strategy provides a sustainable and natural way to improve glucose control.
CLINICALLY-BACKED NATURAL COMPOUNDS

1. Astragalus Root Extract
Improves insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism by modulating AMPK pathways (Li, 2017; Cheng, 2012).
2. Grape Seed Extract
Reduces oxidative stress and inflammation linked to insulin resistance (Zern, 2005).
3. Guarana
Increases energy metabolism and supports glucose regulation (Espinola, 1997).
4. Green Tea Catechins
Enhance insulin action and reduce blood glucose levels post-meal (Nagao, 2005).
5. Gymnema Sylvestre
Shown to regenerate pancreatic β-cells and reduce sugar absorption in the intestines (Baskaran, 1990).
6. Forskolin
Activates cAMP and improves glucose metabolism via enhanced mitochondrial activity (Seamon, 1981).
7. Bitter Melon
Mimics insulin and increases glucose uptake in cells (Sridhar, 2008).
8. Raspberry Ketones
Improve insulin sensitivity and support lipid-glucose balance (Morimoto, 2005).
9. Korean & Panax Ginseng
Reduce fasting glucose levels and improve HbA1c in type 2 diabetics (Reay, 2005; Attele, 2002).
10. Cinnamon Extract
Enhances insulin receptor sensitivity and glucose uptake (Khan, 2003).
11. Capsaicin
Improves glucose handling and enhances fat oxidation (Kang, 2007).
12. Chromium Picolinate
Facilitates insulin action and stabilizes blood sugar levels (Anderson, 1997).
13. Beta-Alanine
Supports glucose transport and insulin response during metabolic stress (Derave, 2007).
14. GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid)
Improves insulin secretion and reduces glucose variability (Adeghate, 2008).
15. L-Tryptophan
Modulates insulin release and affects carbohydrate metabolism (Markus, 2005).
16. Maca Root
Supports energy metabolism and may help improve glucose control (Oshima, 2006).
17. Eleuthero (Siberian Ginseng)
Shown to reduce postprandial glucose spikes and support adrenal balance (Cicero, 2004).
18. L-Arginine
Improves insulin sensitivity and endothelial function (Lucotti, 2006).
🧬 MULTI-AXIS GLUCOSE SUPPORT STRATEGY

This nutrient blend forms a metabolic matrix that works across five essential axes:
- Cellular Glucose Uptake
- Insulin Signaling Pathways
- Mitochondrial Energy Production
- Pancreatic β-Cell Health
- Oxidative Stress Reduction
Together, these functions create a more balanced, adaptable metabolism and smoother glucose control throughout the day.
🧠 WHY IT MATTERS AFTER 40
After age 40, your body:
- Produces less insulin
- Loses mitochondrial efficiency
- Becomes more resistant to glucose transport
- Experiences greater oxidative and inflammatory stress
This leads to:
- Energy crashes
- Brain fog
- Sugar cravings
- Slower recovery from meals
Natural glucose modulators can help rebalance these systems and promote sustainable metabolic health.
🧩 THE DAILY SUPPORT PROTOCOL
Most clinical protocols recommend:
- Once or twice-daily use
- Empty stomach intake for absorption
- Minimum 4–8 weeks for full results
Users report:
✅ More stable energy throughout the day
✅ Fewer sugar cravings and post-meal slumps
✅ Improved focus and mood
✅ Better fasting glucose levels
SAFETY & COMPATIBILITY
These ingredients are:
- GRAS-certified and well-studied
- Non-stimulant and non-habit-forming
- Safe for use alongside diet and exercise changes
They can also be combined with:
- Intermittent fasting
- Low-glycemic diet
- Daily walking or light movement
Magnesium and omega-3 supplementation

CONCLUSION: A SMARTER PATH TO METABOLIC CONTROL
Blood sugar management isn’t just about cutting carbs.
It’s about understanding how your metabolism works — and supporting it with compounds that fuel, regulate, and protect your body’s most critical systems.
Thanks to breakthroughs in natural metabolic science, you can:
- Regain metabolic flexibility
- Improve insulin function
- Reduce sugar crashes
… all without harsh interventions or side effects.
🧾 REFERENCES
- “The Role of Astragalus Membranaceus in Glucose Metabolism and Insulin Sensitivity” – Li W, et al. (Journal of Medicinal Plants Research, 2017)
- “Antidiabetic Properties of Grape Seed Extract: Effects on Insulin Resistance” – Zern TL, et al. (Journal of Nutrition, 2005)
- “Impact of Guarana on Glucose Regulation and Energy Metabolism” – Espinola EB, et al. (Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research, 1997)
- “Effects of Green Tea Catechins on Blood Glucose Levels and Metabolic Health” – Nagao T, et al. (American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 2005)
- “Gymnema Sylvestre and Its Influence on Blood Glucose Control” – Baskaran K, et al. (Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 1990)
- “Forskolin and Its Role in Glucose Metabolism” – Seamon KB, et al. (Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 1981)
- “The Efficacy of Bitter Melon (Momordica charantia) in Lowering Blood Glucose Levels” – Sridhar MG, et al. (Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 2008)
- “Raspberry Ketones: Mechanisms of Action in Glucose Uptake and Fat Metabolism” – Morimoto C, et al. (Planta Medica, 2005)
- “The Influence of Korean Ginseng on Blood Sugar Levels in Type 2 Diabetes”– Reay JL, et al. (British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 2005)
- “Role of Cinnamon Extract in Glucose Regulation and Insulin Sensitivity” – Khan A, et al. (Diabetes Care, 2003)
- “Panax Ginseng: Its Role in Blood Glucose Management and Insulin Sensitivity” – Attele AS, et al. (Diabetes Care, 2002)
- “Capsaicin’s Impact on Blood Sugar Control and Its Potential Antidiabetic Effects” – Kang JH, et al. (Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2007)
- “Chromium Picolinate and Its Effectiveness in Blood Sugar Management” – Anderson RA (Diabetes, 1997)
- “Beta-Alanine and Its Role in Enhancing Insulin Sensitivity and Glucose Uptake” – Derave W, et al. (Journal of Applied Physiology, 2007)
- “Role of GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid) in Insulin Secretion and Glucose Homeostasis” – Adeghate E, et al. (Endocrine Reviews, 2008)
- “L-Tryptophan and Its Potential Role in Insulin Regulation” – Markus CR, et al. (Psychosomatic Medicine, 2005)
- “Maca Root (Lepidium meyenii) and Its Potential Benefits on Glucose Homeostasis” – Oshima M, et al. (Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 2006)
- “Eleuthero (Siberian Ginseng) and Its Effect on Blood Glucose Levels” – Cicero AF, et al. (Fitoterapia, 2004)
- “L-Arginine’s Impact on Glucose Tolerance and Insulin Sensitivity” – Lucotti P, et al. (Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 2006)
- “Astragalus Root Extract: Effects on Insulin Resistance and Glucose Metabolism” – Cheng YC, et al. (Phytotherapy Research, 2012)